Today I would like to show you how to set up a Siemens Scalance S615 firewall. This configuration allows you to access a plant network from a company network. You can do this without both networks having the Scalance entered as the default gateway.
Setup
PC 192.168.10.179 (VLAN 2 EXT) NO Gateway
SCLANACE 192.168.1.1 (VLAN 1 INT) and 192.168.10.1 (VLAN 2 EXT)
MACHINE 192.168.1.99 (VLAN 1 INT) NO Gateway
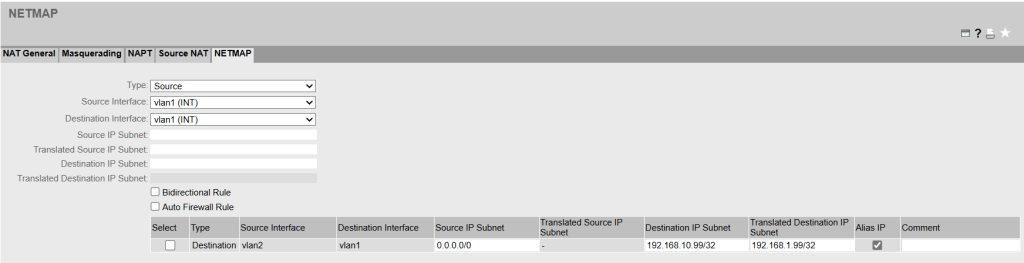
1. NETMAP
The PC communicates with 192.168.10.99 (Alias IP) from its own network, which is translated using a destination NAT. The machine behind this is 192.168.1.99.
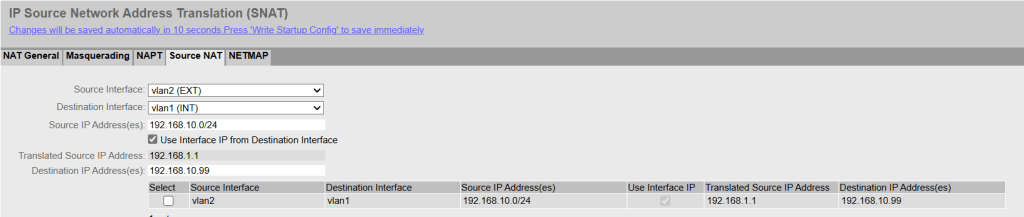
2. Source NAT
The machine thinks the packet comes from 192.168.1.1 (Source NAT) and can send a response packet without a gateway because it thinks the packet comes from the same subnet.
3. Firewall Rule
Don’t forget to set the corresponding entry in the firewall rules. „Auto Firewall Rule“ in the NETMAP can be helpful to automatically create an entry, but with a custom or customized entry the rule can be formulated more specifically.
Terms
Announce alias IP addresses
- Sends a gratuitous ARP to announce the IP address.
- This happens without an ARP request when creating NAT rules or rebooting the appliance.
Alias IP
- NAT IP is registered on the source or destination interface.
- CAUTION with entire subnets! In combination with „Announce Alias IP addresses,“ each IP address is announced on the network with the MAC address of the router interface. This could produce a network outage.
BIDIRECTIONAL Rule
- Enters a second rule from the other direction.
- This is important if the other side also wants to initiate the connection.